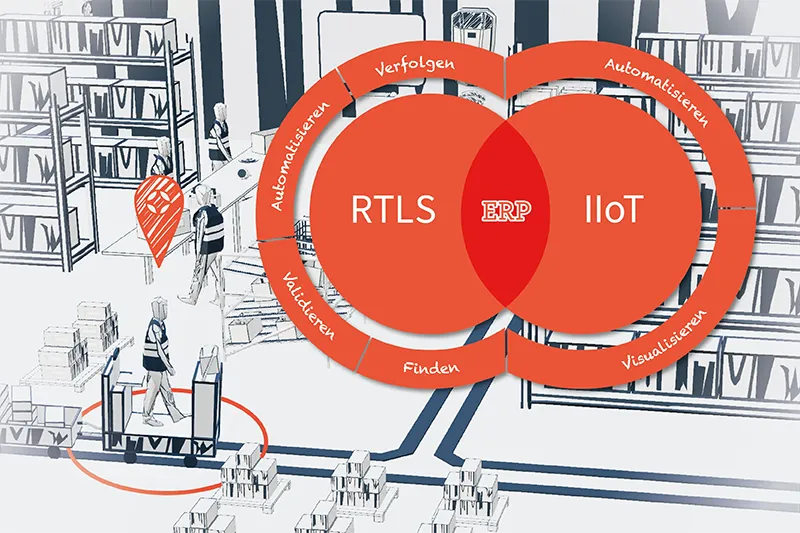
Industry 4.0 enables a variety of process optimizations within production and logistics to be able to design production processes effectively. The added value of RTLS and IIoT is presented below using a possible use case.
What is RTLS and IIOT
With a “Real Time Locating System” objects and people can be located and tracked in real time. This data can be integrated and used directly into an SAP system (e.g. EWM). The real time locating system can e.g. B. as Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID), as Ultra Wideband (UWB) or as Bluetooth to precisely determine the position. Interoperability between the individual transmission technologies is only possible with “omlox” from Trumpf. The precise location and tracking of objects and people makes it possible to optimize operational processes and increase productivity.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is an industrial variant of the Internet of Things (IoT) and refers to the networking of industrial devices, machines, sensors and other objects in the production environment. Using Internet and data analytics technologies, IIoT enables the collection, analysis and use of data in real time to increase efficiency and productivity in production. The SAP system is the central “control unit” with which the processes are controlled, initiated or documented. IIoT solutions include, among other things, the monitoring and control of systems using sensors as well as the optimization of production and logistics processes. This enables the fourth industrial revolution, also known as “Industry 4.0”. The level of integration of the RTLS and IIoT components can be individually configured and connected to the SAP system depending on the needs and benefit ratio.
The following components are available:
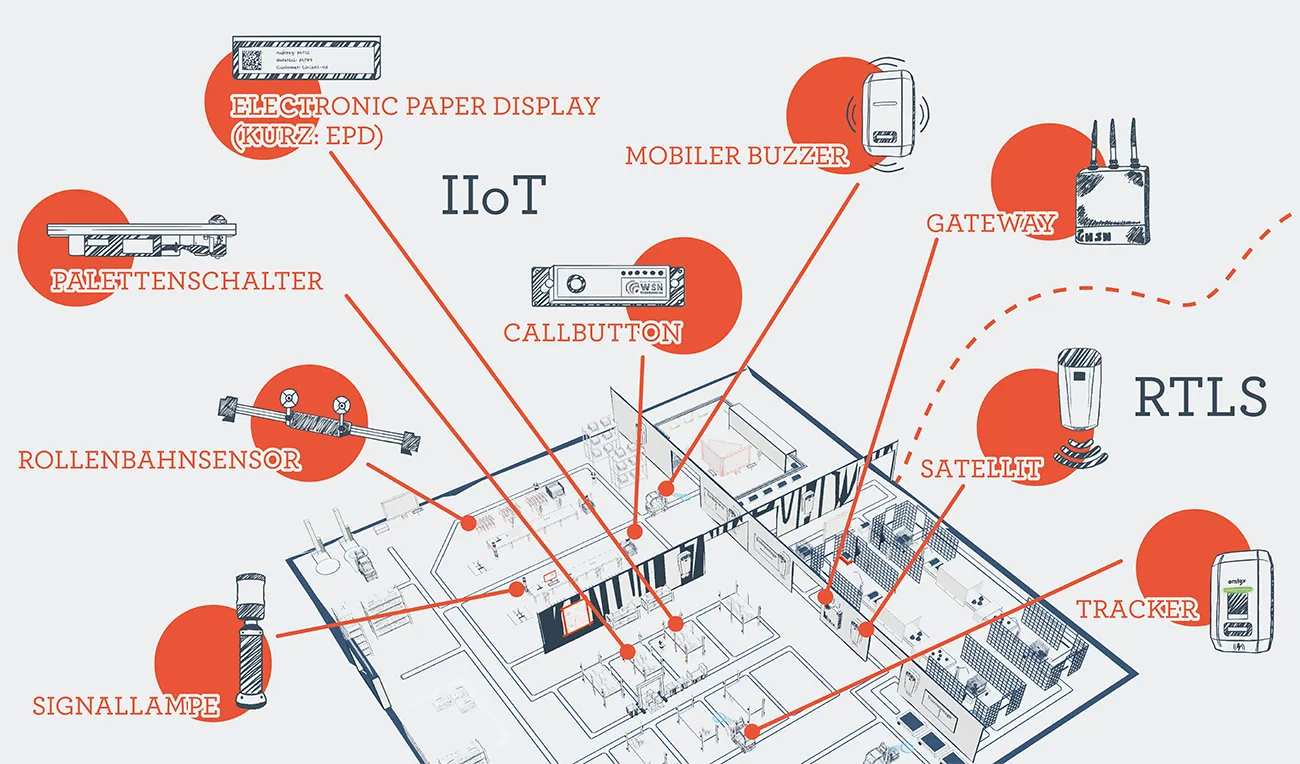
Tracker
- Locates objects, vehicles or people.
Satellites
- Locates UWB signals. Is calibrated and synchronized with other satellites.
Roller conveyor sensor
- The sensor records and reports the document status in roller conveyor shelves to the ERP system and is therefore essential for the automation of replenishment processes such as eKanban.
Signal lamp
- Occupancy statuses, dangers or the fastest route through the factory can be displayed using a light signal using a multifunctional light.
Electronic Paper Display (short: EPD)
- EPDs are small electronic labels and display status information of the containers to which they are attached. LEDs support the display as soon as an event occurs, for example by lighting up green or red.
Call button
- When you press the call button, defined information is transmitted or reported back to, for example, an SAP system. These states can also be displayed visually via the LEDs or a display.
Pallet switch
- The sensor records the occupancy of parking spaces. This enables active management of spaces and control of replenishment.
Mobile Buzzer
- The buzzer triggers a defined event and indicates this by vibrating or lighting up an integrated lamp (depending on the model).
Gateway
- The gateway is a media converter and serves as an interface between sensor and actuator end devices.
Advantages of RTLS and IIOT
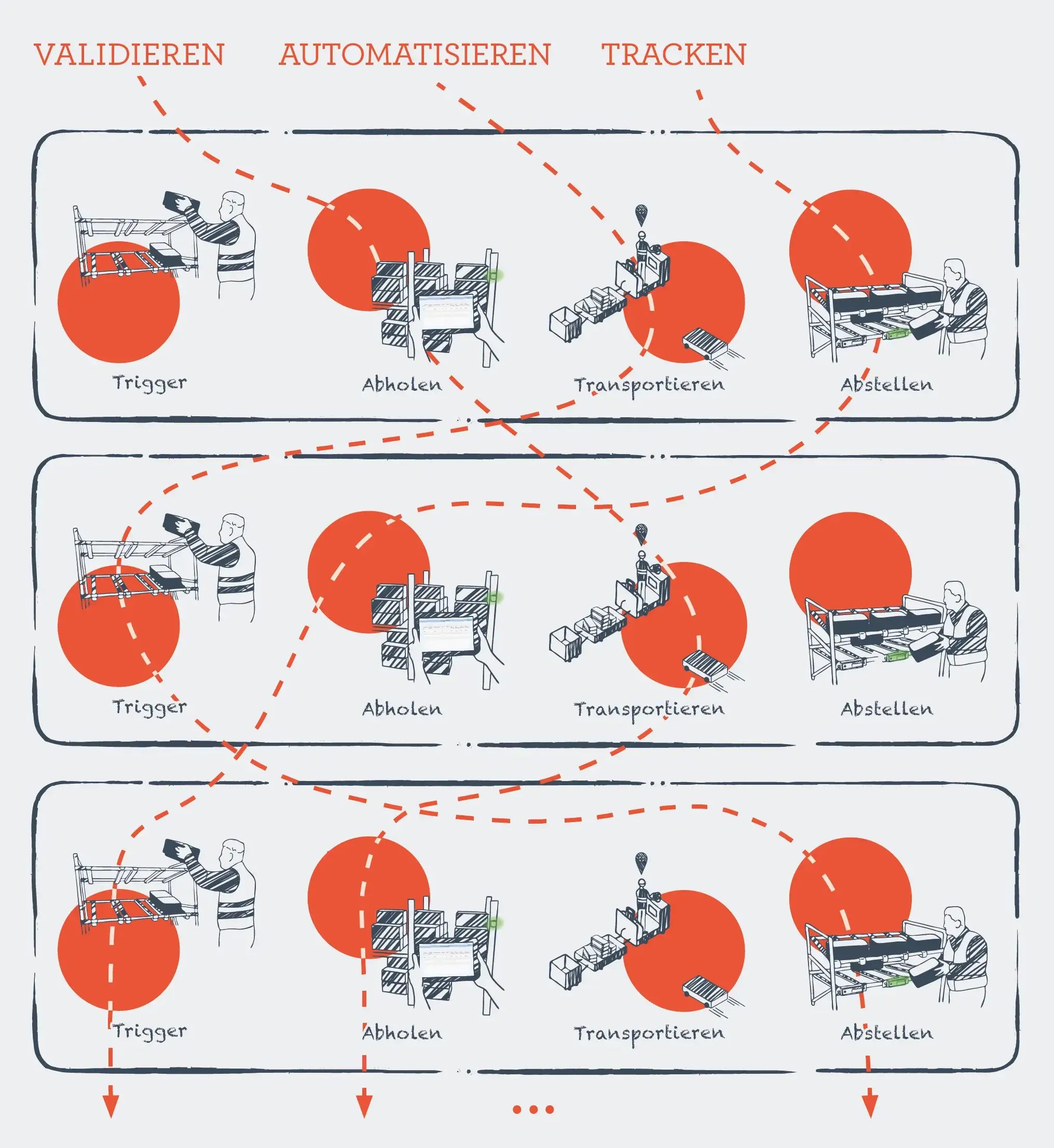
The combination of RTLS and IIoT in the SAP system landscape makes it possible to record a condition that serves as a trigger for a replenishment process. The replenishment process can be divided into three sub-processes: collection, transport and storage. Validation, automation, and discovery are discussed below in the context of the replenishment process:
The replenishment process can be triggered by various sensors:
- The replenishment process can be triggered by removing a pallet from the central warehouse. The pallet sensor records the removal and sends the status to the SAP system. Based on the change in status, an automated action (warehouse task for replenishment) can take place.
Support in the in the collection process and in finding relevant supplies:
- By comparing the real-time position data of material and the logistics employees, the LEDs on the Electronic Paper Display can be controlled by the SAP system as soon as the employee is close to the replenishment material to be picked up. This pick-by-light solution makes finding things easier and saves you having to search for the right replenishment material.
Support in the transport process by automating the physical movement of goods:
- By removing a pallet from the central warehouse using sensors, a warehouse task can be created in the SAP system that carries out a physical movement of goods fully automatically using driverless transport systems (AGVs). The corresponding warehouse task is automatically confirmed based on the position data of the material in the SAP system.
Support in the parking process by validating position data:
- With the automatic transport of the automated guided vehicle system (AGV), the material can be located within a day. The SAP system continuously checks the target storage location from the EWM warehouse task. This is automatically acknowledged as soon as the current location of the material matches the target location.
UseCase
The following process is a possible scenario with which RTLS and IIoT components can be integrated to support employees in production and logistics and to be able to carry out the processes more effectively:
Removing the material from the eKanban shelf acts as a trigger in triggering the sensor. When the sensor is triggered, requirements are automatically generated in the SAP system and a corresponding warehouse task is created in the EWM system. In this case, the sensor knows exactly what material it is because each shelf compartment is assigned a specific material. The EWM system is a logical 1:1 image of the production factory and each virtual EWM storage location reflects a physical storage location.
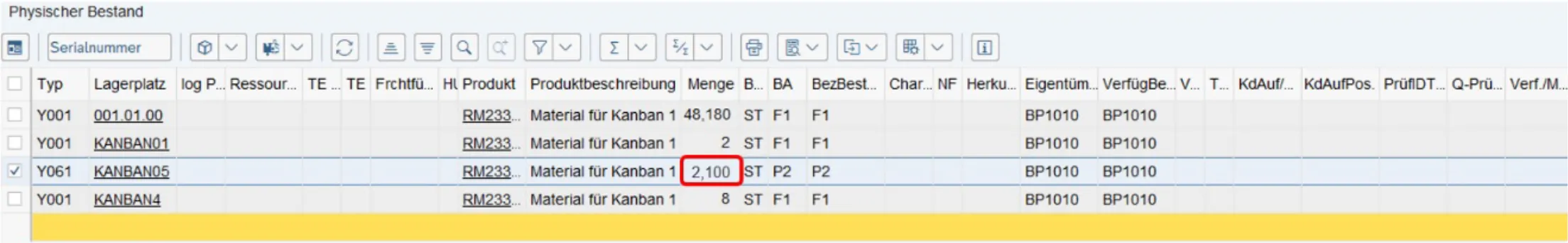
EWM-Status monitor before removing the box
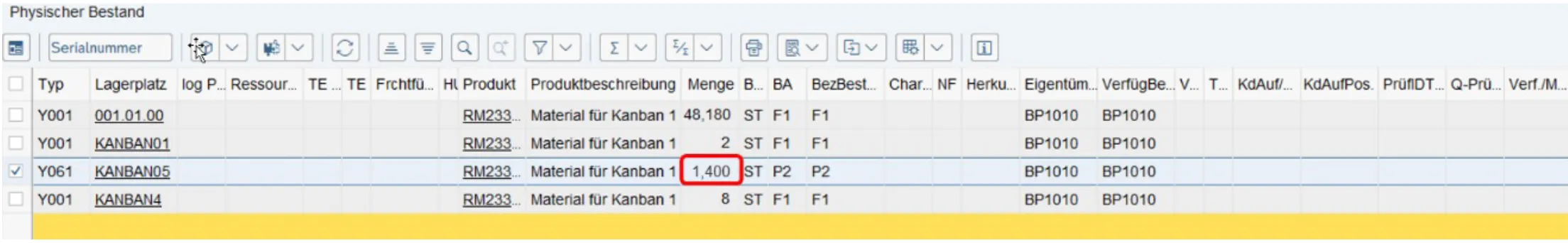
EWM status monitor: Reporting stock of 3 boxes of 700 materials each reached and automatic creation of a warehouse task
- The logistics employee in logistics receives a push notification on the handheld device and selects the EWM warehouse task from the queue that was automatically created when the box was removed. The employee can be located using a tag and UWB technology. The associated material from the warehouse task is also located using UWB technology. The continuous management and monitoring of position data is managed by the SAP system as a central unit and evaluated depending on the process.
- By comparing the position data of the material from the warehouse task and the employee, the distance between the material and the logistics employee can be determined exactly. The Real Time Locating System helps the logistics employee find the right material by having LEDs on an Electronic Paper Display (EPD) light up green when the employee approaches. When the box is physically removed, the system uses UWB technology to recognize the removal and automatically acknowledges it in the warehouse task in the EWM system.
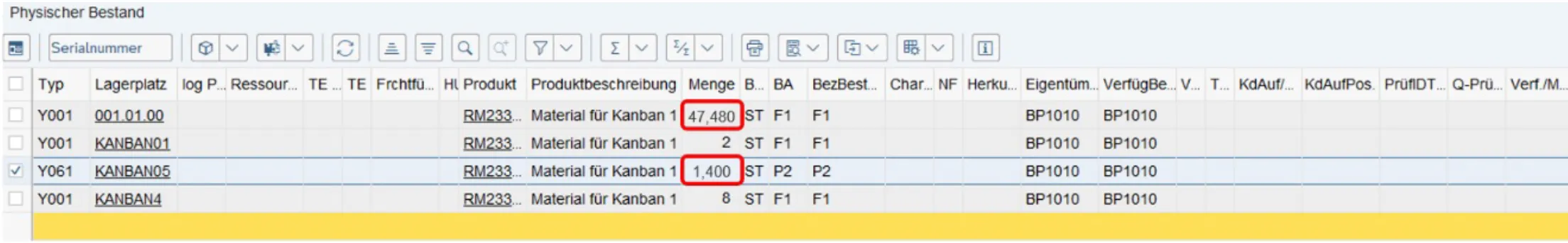
Removal of the box from storage location 001.01.00 and automatic confirmation of the EWM warehouse task.
- If the next logistics employee places the box in the wrong place, the system detects this error based on the position data and warns with red LEDs on the Electronic Paper Display (EPD). The warehouse task is also noted on this and the note “Incorrectly parked! Please bring to zone B” appears on the display and it is not possible to confirm the warehouse task.
- When you leave the incorrect storage zone, the Real Time Locating System uses UWB technology to revoke the notice. The position of the shelf is known and can be used accordingly by the real time locating system. When the employee approaches the eKanban shelf, the person is supported by put-to-light technology. Here the LEDs on the call button light up green as soon as the distance is less than 3 meters. When the storage location is filled, the eKanban sensor detects this and reports the filling of storage location KANBAN05 to the EWM system.
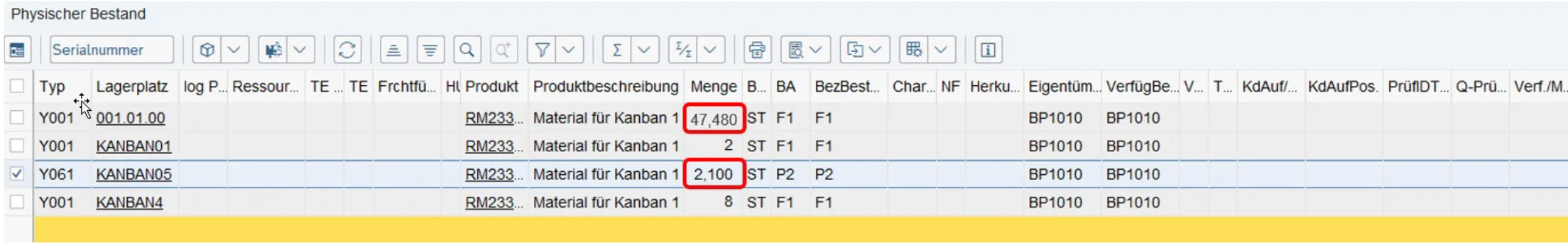
Filled EWM storage space after feeding the material and detecting the shelf sensor in the eKanban shelf
Experience further possible applications at digitalisierung.inwerken.de or contact us. If you have any questions about RTLS, simply write to sapberatung@inwerken.de. If you have IIoT topics, please contact info@wsntec.com.