There has been the convenient option of creating CDS views in Eclipse and publishing them via annotation on the SAP Gateway since SAP Netweaver 7.4 SP05. Using the available templates in the SAP WebIDE, you can easily generate an interface for the CDS views. This creates a complete SAP Fiori application with just a few lines of code. But the disadvantages quickly become clear in the attempt to expand the application generated this way:
In the project, one searches in vain for the well-known XML views or JavaScript controllers.
The following section describes how to integrate a CDS view with associated metadata extension into an existing SEGW project. The standard UI5 Smart Controls are then used in a classic UI5 application to consume this data. The resulting UI5 application combines the advantages of CDS views with those of manual development.
Application
For the present example, an app is used in a List Report Layout. By subsequent adjustments, the app is personalized with XML and JavaScript.
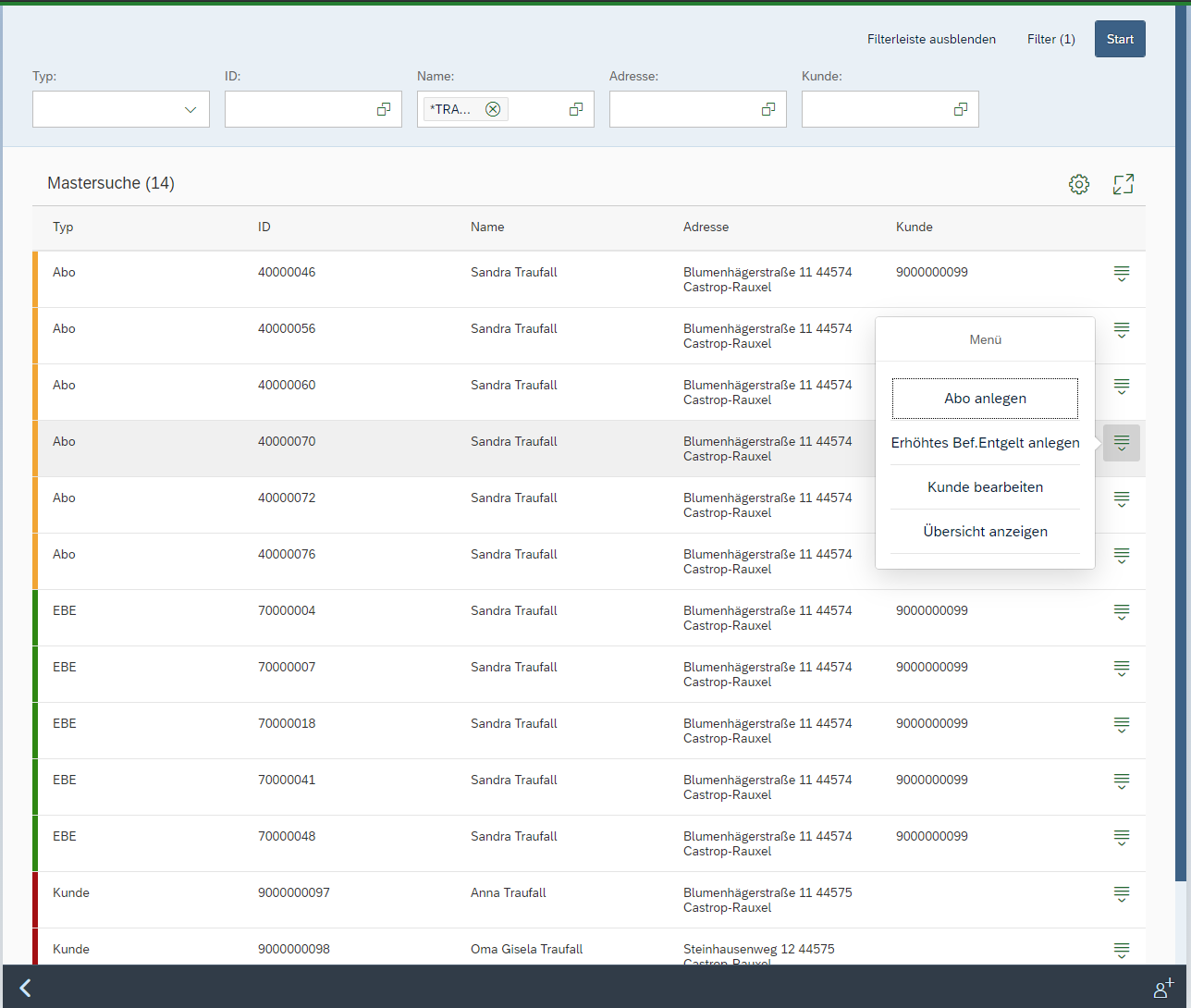
Figure 1: Final List Report Application
Creating the CDS Views
The basis of the CDS Consumption Views ‘ZMASTERSEARCH’ is a variation of interface views. Since the topic of the structure of CDS views is described sufficiently and it will not be discussed any further.
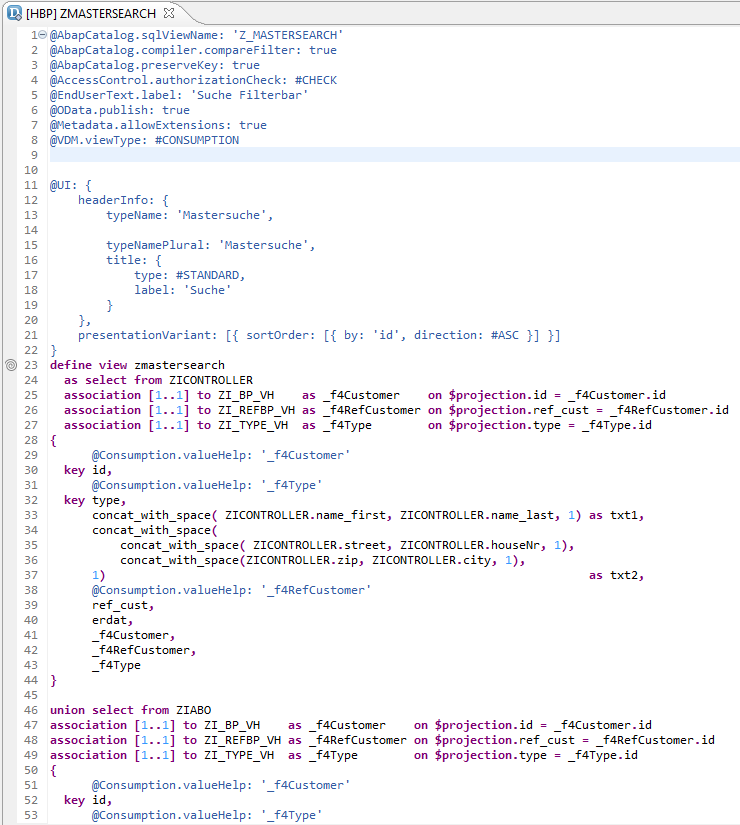
Figure 2: Excerpt of the Consumption Views ZMASTERSEARCH, which is used below for our Application.
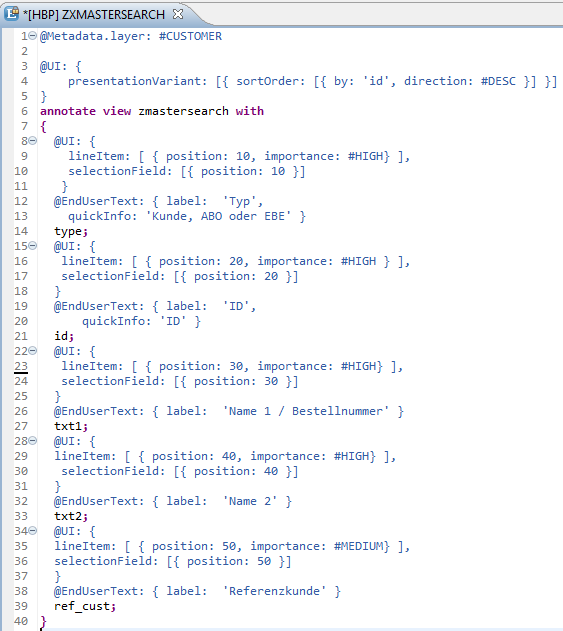
Figure 3: Metadata Extension for ZMASTERSEARCH
Creating the SEGW project
An existing SEGW project will be extended by the Consumption View:
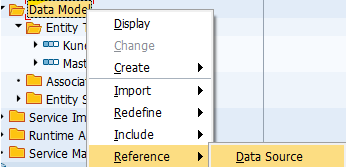
Figure 4: SEGW
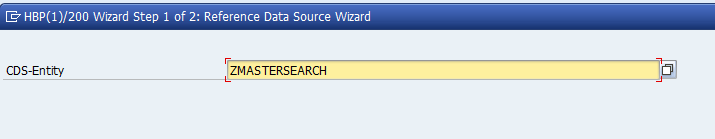
Figure 5: Selecting the CDS Views
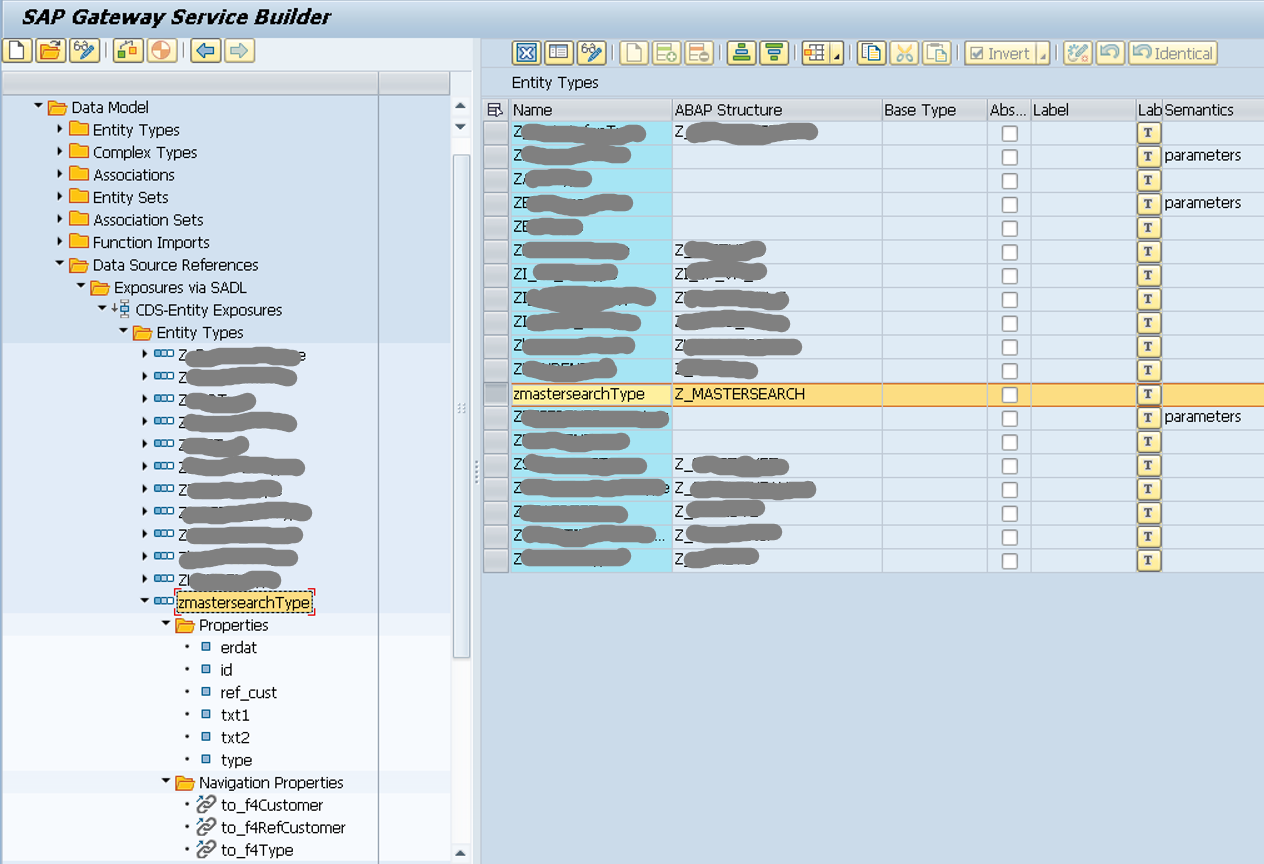
Figure 6: SEGW and CDS
The entity can be reached through the service after regenerating the project.
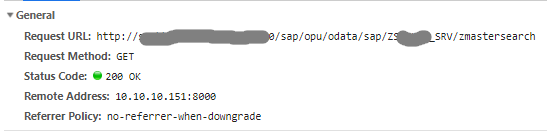
Figure 7: SuccessfulRead on the CDS View
The Consumption View is thus integrated in the SEGW project and can be used in the UI5 application.
Annotation service
The annotation from the gateway must be provided in addition to the data for later use in the UI5 application. After the CDS View has been integrated into the SEGW and the project has been activated, the annotation model appears under the runtime artifacts.
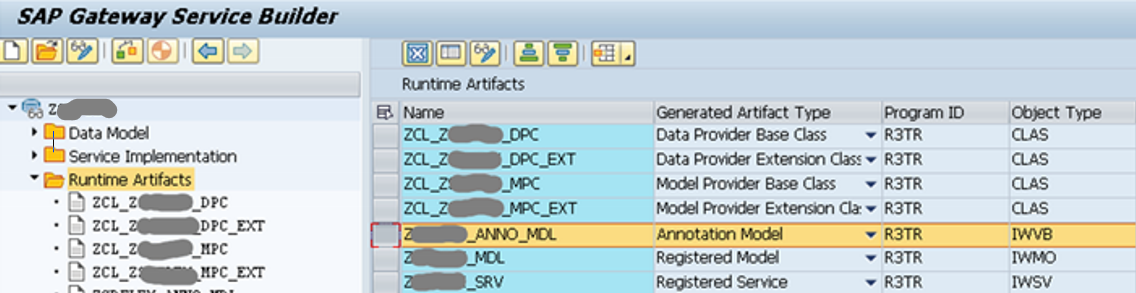
Figure 8: Runtime Artifacts
The annotations can be displayed via the SAP Gateway Client and downloaded with a browser. The transaction / N / IWFND / MAINT_SERVICE is called and the Gateway Client is started.
Figure 9: Service Catalogue
Figure 10: Annotation
https://:/sap/opu/odata/IWFND/CATALOGSERVICE;v=2/Annotations(TechnicalName=’_ANNO_MDL’,Version=’0001′)/$value
The annotations can be downloaded and be used locally.
Creating the UI5 application
At the beginning of the development it makes sense to load a current template from the WebIDE.
Figure 11: Templates in WebIDE
In the new application, the manifest.json is adjusted first, so that in addition to the metadata also access to the annotation exists.


Figure 12: Custom manifest.json
Annotation and metadata are inserted into the application in a known way.

From this point you have a fully functional UI5 List Report application that has all the functions defined in the template and CDS View.
Consumption of the CDS views in the application
The view of the UI5 application gets a Smart Filter Bar and a Smart Table Control. Both controllers are assigned the zmastersearch entity set.
The sap.m.Table within the SmartTable provides color highlighting of the result types (highlight = “{path: ‘type’, formatter: ‘. Formatter.lineHighlighter’}”).


Figure 15/16: Custom Smart Controls in the View
Subsequently, the Smart Table can be adjusted by the usual means. In this example, the row type has been manipulated and appropriate handlers inserted.
Author: Tobias G.